Boiler water quality has long been an important factor in the operation of boilers. As the power plant operating pressures increase, water quality requirements also become stricter. With the current units operating at Supercritical pressures, the requirements are tough. Continuous improvements and changes in the methods of maintaining water quality, understanding the corrosion mechanisms, and the development of new chemicals have resulted in a more economical and efficient water regime management.
Four Reasons Why Boiler Water Treatment is Important
There are four main reasons why water quality is so important. Impurities in water form scales.
- Water contains dissolved salts, which upon evaporation of water forms scales on the heat transfer surfaces. Scales have much lower heat transfer capacity than steel: the heat transfer coefficient of the scales is 1 kcal/m/°C/hr against 15 kcal/m/°C/hr for steel . This leads to overheating and failure of the boiler tubes. Scale also reduces flow area, which increases pressure drop in boiler tubes and piping.
- Low pH or dissolved oxygen in the water attacks the steel. This causes pitting or lowering the thickness of the steel tubes, leading to rupture of the boiler tubes. Contaminants like chlorides, a problem in seawater cooled power plants, also behave in a similar way.
- Flow assisted corrosion occurs in the carbon steel pipes due to the continuous removal of the protective oxide layer at high flows.
- Impurities carried over in the steam, causing deposits on turbine blades leading to reduced turbine efficiency, high vibrations, and blade failure. These contaminants can also cause erosion of turbine blades. Silica at higher operating pressures volatilizes and carries over to the turbine blades.
The first step is to get the make-up water to the steam cycle as pure as possible. The correct operation of the De-Mineralisation (DM) plants ensures this.
The second step is to form a magnetite layer on the inside surface of the tubes which protects the metal surface from any further corrosion attacks.
The third step is to maintain this magnetite layer throughout the life of the plant.
If the water quality goes down, this protective layer will be destroyed and corrosion starts damaging the tubes.
In a 500 MW power thermal plant around 1300 Tons of water is circulating per hour continuously in the water steam cycle through the boiler, turbine, condenser and heaters. As the water circulates, there is an increase in contaminant level and a change in water quality. This is due to many reasons like:
- contact with almost 25000 m² area of wetted steel in the tubes, piping and heat exchangers
- the residue of chemicals added
- entrapped oxygen and other gases especially in the vacuum area
- returning condensate from traps, glands, vents and drains
- impurities in the DM water make-up
Major parameters that require monitoring for water treatment are:
- The dissolved solids.
- The pH of the boiler feed water.
- Dissolved Oxygen in the feed water entering the boiler.
- Silica in boiler water.
Water Steam Circuit- Sub Critical vs Super Critcal
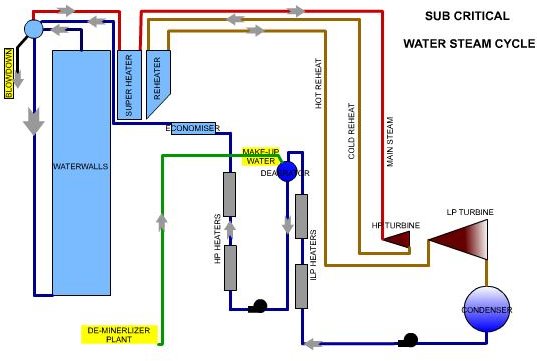
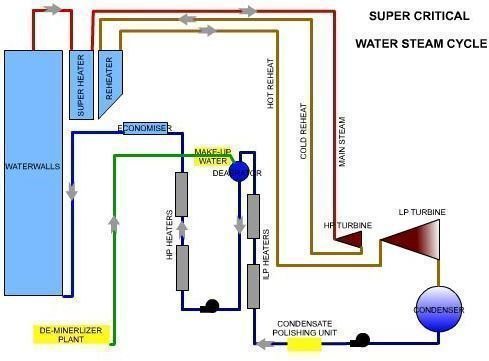
Differences in a Supercritical Unit
The Water Steam circuit in a Supercritical unit is different from that of a sub-critical unit. This makes the water quality requirement more stringent in a Supercritical unit.
In a subcritical unit, water steam separation takes place in the drum. Any contaminants remain in the water. As their concentration level increases, continuous “blow down “removes these. The drum, water walls, and down comers act as a reservoir and an internal circulation circuit and help in concentrating and removal.
- In supercritical once-through boilers this is not possible, which means any contaminants will adhere to the tubes or caries out through the steam. To prevent this, purity of the water entering should be very good. This makes it mandatory to have a full condensate polishing unit before the water enters the heating sections.
PH control is by the addition of chemicals like Tri-Sodium Phosphate in the boiler water or the “caustic treatment." This helps in maintaining the pH levels in the range of 9.0, slightly alkaline. The chemical reactions result in the formation of salts, which increases the dissolved solids level. In subcritical unit, “blow down" removes this.
- This is not possible in supercritical units. So an “all volatile treatment" (AVT) is used. This method uses amines whose reaction products are volatile, leaving behind no solids. This passes along with steam and removal takes place in the de-aerator or polishing systems. AVT is also the new method in subcritical drum type units.
- Super critical units also use the oxygenated treatment (OT) system, which involves injecting a known quantity of oxygen in the feed water. This helps in maintaining the magnetite or hematite layer, which provides the barrier to prevent any further corrosion in the piping and tubes.
- During start-ups and at lower loads where the water chemistry regimes are fluctuating, boiler water control is by the AVT method.
.
Dissolved oxygen removal is in the deaerator where at saturation temperatures oxygen stripping is easier. Addition of hydrazine at the deaertaor outlet also removes the dissolved oxygen if any in the feed water.
- Supercritical units also use deaerators. But some plants using only OT operate without a deaerator.
Silica control can is by blow down in a subcritical unit.
- In Supercritical units the only way is to ensure very low Silica in incoming DM water and good removal in the condensate polishing unit.
As the thermal plant operating pressures increase and become supercritical, water chemistry management also becomes critical. Along with adopting the correct water treatment method, a high quality DM plant and precision analytical instruments for monitoring online water chemistry is a must to eliminate outages of the plant.
For Reference
Water Treatment Solutions – lenntech.com
https://www.brighthubengineering.com/power-plants/116056-importance-of-boiler-water-treatment/